WIFI Knowledge
802.11 Association Process
1. Beacon
The access point periodically sends a beacon frame (every 100ms )to announce its presence and relay many information that is required by the stations to connect to the wireless network
STA begins the process by performing a passive or active scan. In the passive mode, the STA is listening for beacons from an access point. The beacon frame contains the BSSID which is the MAC address of the radio sourcing from the access point.
Beacon packet contains capability information and parameters.
2. Probe Request
Probe requests advertise the mobile stations supported data rates and 802.11 capabilities such as 802.11n.
A probe is sourced from the STA requesting to join a wireless network. The probe is responded by an access point using a probe response management frame. Probe request from a STA broadcasted to any access point that can respond.
3. Probe Response:
APs receiving the probe request check to see if the mobile station has at least one common supported data rate. If they have compatible data rates, a probe response is sent advertising the SSID (wireless network name), supported data rates, encryption types if required, and other 802.11 capabilities of the AP.
4. Authenticated Request
The station chooses a SSID/network from the probe responses it receives. It also checks the compatibility on encryption type. Once compatible networks are discovered the station will attempt low-level 802.11 authentication with compatible access points. The station sends a low-level 802.11 authentication frame to an AP setting the authentication to open and the sequence to 0x0001.
If you noticed in the above successful authentication frame, the Authentication Algorithm was set to Open System. There are two types of methods for authentication.
- Open System: WPA, WPA2 with no password, performs no client verification.
- Shared Key: passphrase and contains a 4-way handshake for authentication. The STA sends a request to authenticate, access point receives the request and sends back a cleartext challenge, the STA encrypts and sends another authentication request based on the cleartext challenge and then the access point compares the STA’s challenge to the text. If successful, the STA is authenticated.
5. Authenticated Response
STA can be in either two states in Authentication and Association:
- Unauthenticated or authenticated.
- Unassociated or associated.
The access point receives the authentication frame and responds to the station with authentication frame set to open indicating a sequence, If an access point receives any frame other than an authentication or probe request from a station that is not authenticated it will respond with a deauthentication frame placing the mobile into an unauthenticated an unassociated state. The station will have to begin the association process from the low level authentication step. At this point the station is authenticated but not yet associated
6. Association Request
Once the station determines which access point it would like to associate to, it will send an association request to that access point. The association request contains chosen encryption types and other compatible 802.11 capabilities.
7. Association Response
If the elements of the association request match the capabilities of the access point, it will create an Association ID for the mobile station and respond with an association response with a success message granting network access to the mobile station.
Association Response includes:
- Capabilities Information such as
- Supported Data Rates
- HT Capabilities
- HT Information such as the Primary Channel
- WMM information
WPA personal vs enterprise
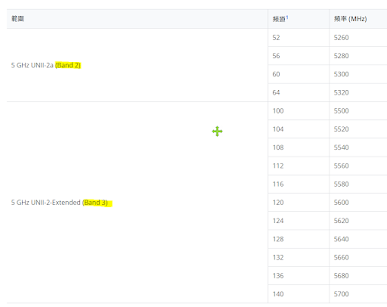
DFS Dynamic Frequency Selection
If the device
is already operating on a DFS channel and radar signals are detected you will
encounter disconnection, however the connection can
be restored after a while. But you may see the change in the operating channel.